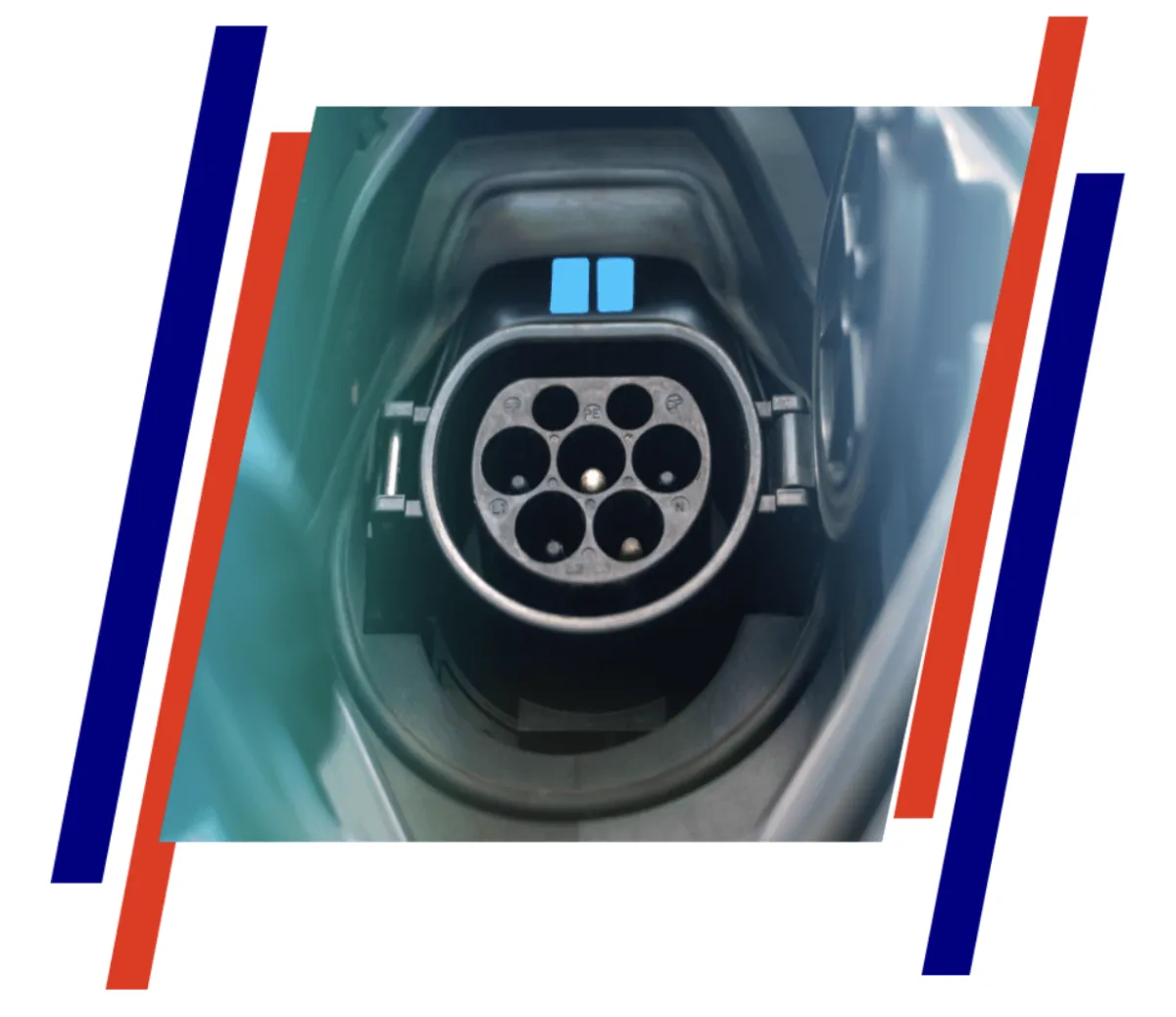
Life-Saving EV Safety
Training for First Responders
& EV Auto Technicians
When seconds count, safety is everything. MyXEV offers the most comprehensive electric vehicle (xEV) training available, ensuring that first responders, automotive technicians, and EV enthusiasts are fully prepared to excel in the ASE certification test. With MyXEV, you don’t just learn—you master the skills needed to navigate the high-voltage dangers of electric vehicles and hybrids, so you can confidently earn your ASE certification.
Home EV Charger Safety
Prepare yourself for stationary related electrical accidents

EV Safety Certification Prep
Prepare for the official Certification
Course
Mobile Incident Safety
Prepare for handling EV incidents in the field
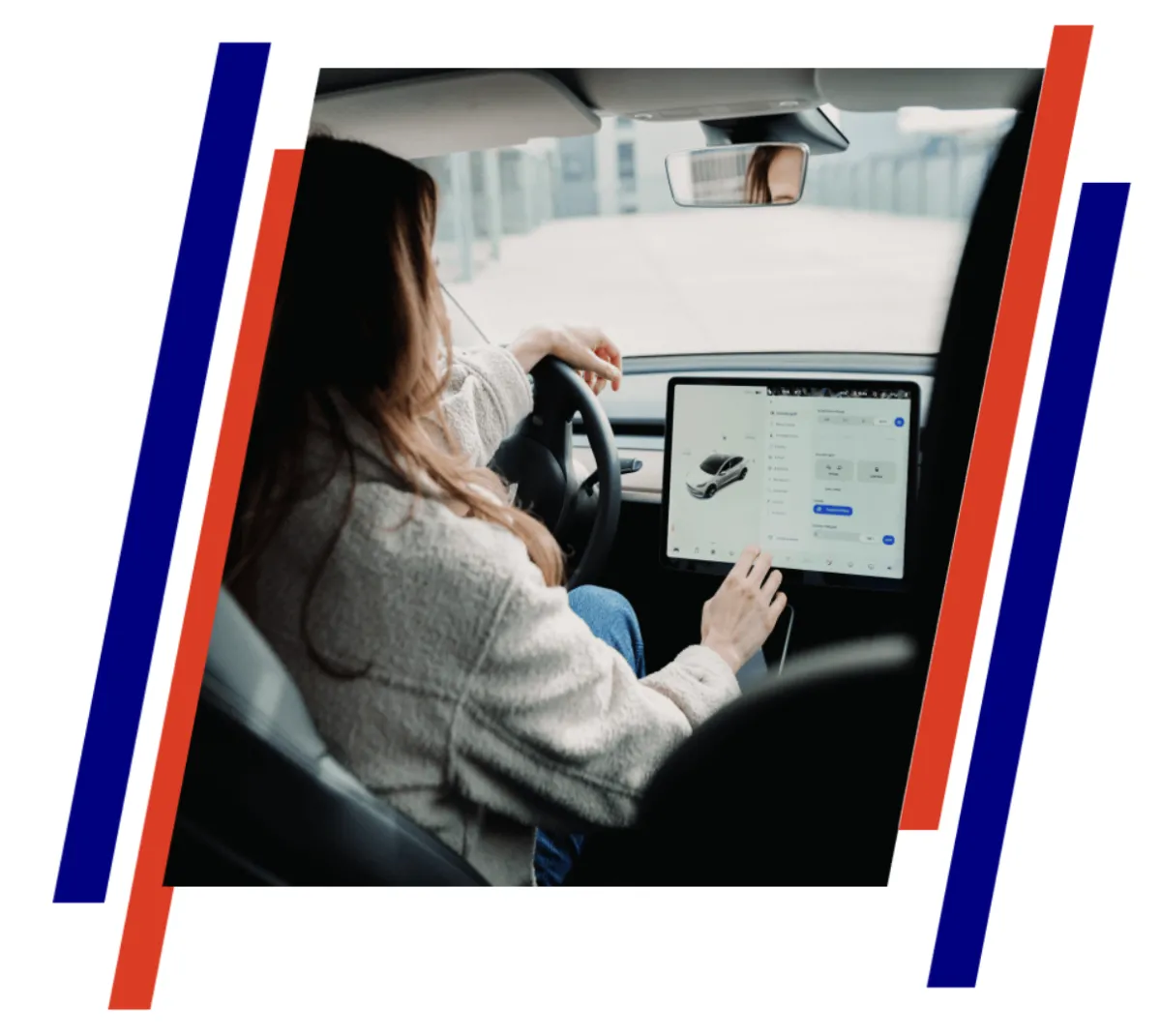


KEEPING FIRST RESPONDERS, TECHNICIANS, AND FAMILIES SAFE
Electric vehicles or “EVs” are the future of transportation for millions of people across the globe, but with an advancement in technology comes an information gap that is putting the lives of our bravest in danger every single day, on each and every call.
Whether you’re preparing for the ASE course member certification or brushing up on electric vehicle safety protocols, MyXEV has you covered. Our courses are crafted by industry experts who understand the unique challenges of working with electric and hybrid vehicles. With us, you’ll gain the critical knowledge needed to safely handle high-voltage systems—both in the classroom and on the field.

SERVING THOSE WHO SERVE
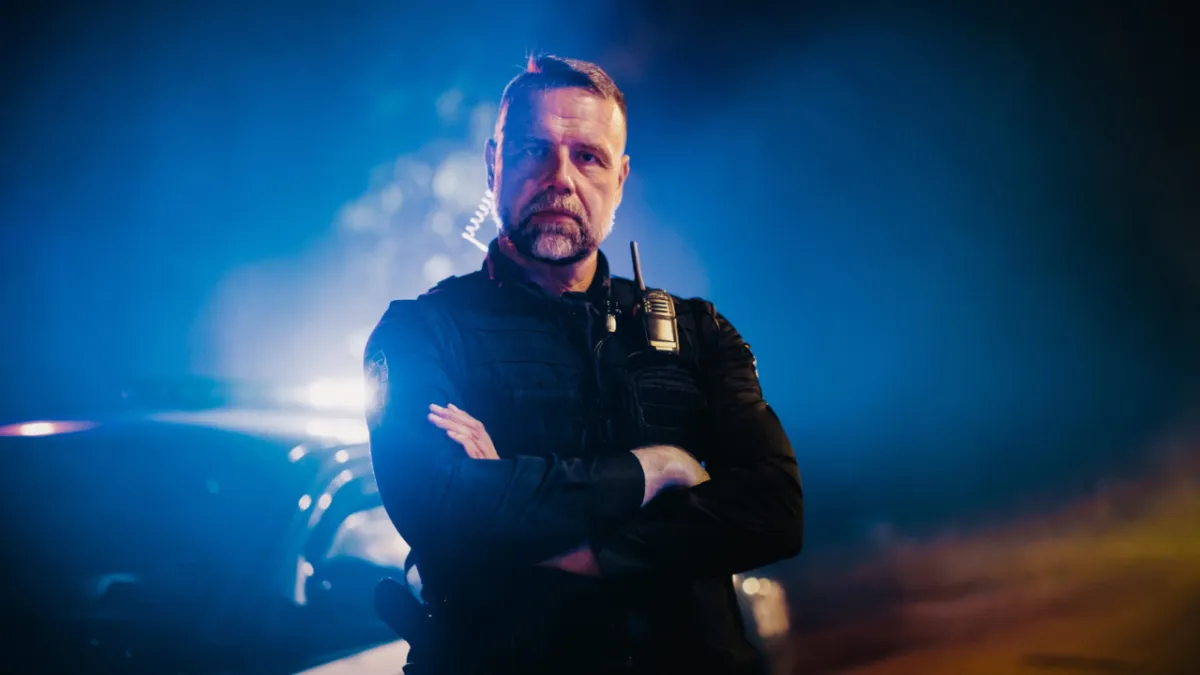

Police Response Training
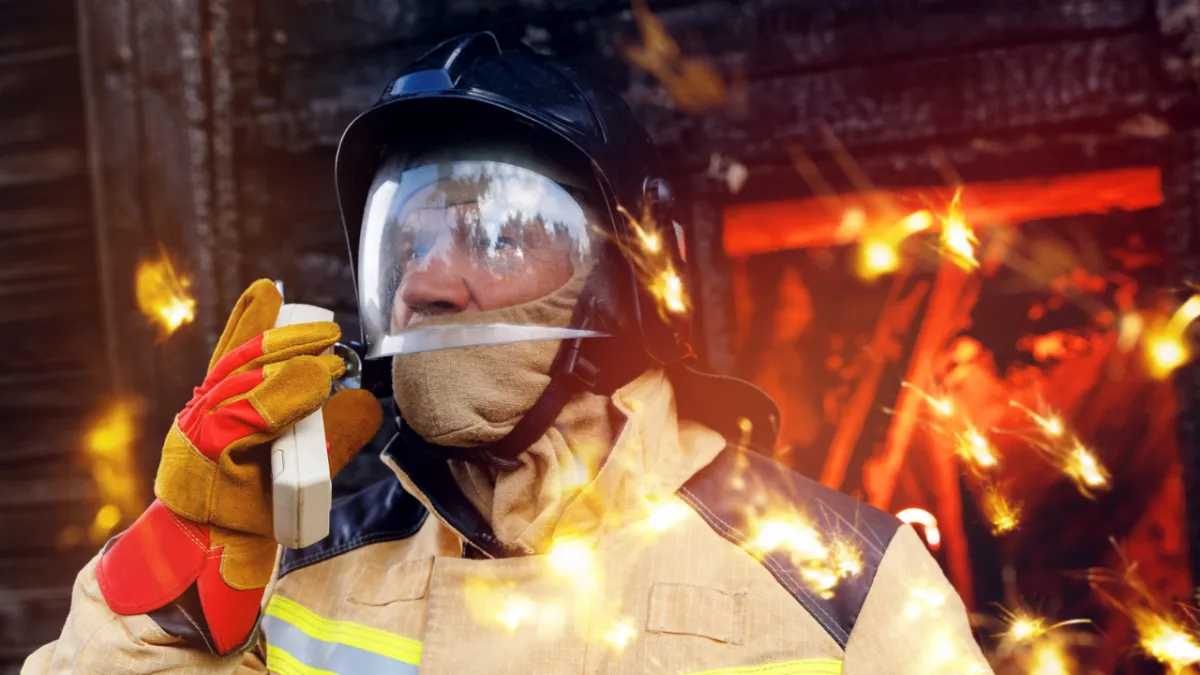

Fire Department Training
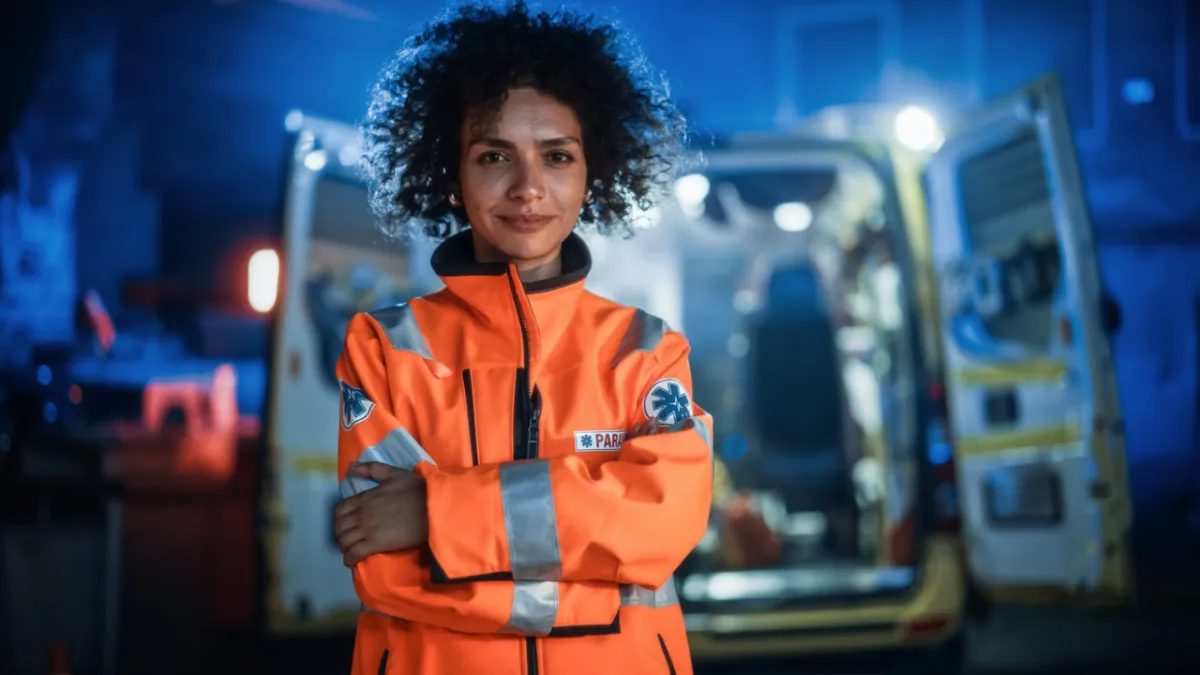

Paramedic Training
Every Model, Every Make








Why Choose MyXEV?
99% Pass Rate: Our Course Members have a remarkable 99% pass rate on the ASE automotive certification, making MyXEV the premier choice for ASE test prep. Our program is meticulously designed to align with the ASE Electrified Propulsion Vehicles (xEV) standards, ensuring you’re not just ready, but over-prepared for the ASE certification online.
Learn Anytime, Anywhere: Our online platform allows you to access ASE certification online training at your convenience, offering flexibility without sacrificing quality. Whether you’re a busy first responder or an automotive technician looking to advance your career, MyXEV’s electric vehicle training fits your schedule.


